Have you ever clicked on a link to a website and ended up with an error page? It can be frustrating, especially if you were excited to read a particular blog post or make a purchase. If you have a WordPress website, you might have experienced this issue before. One of the most common reasons for this problem is incorrect or broken permalinks. In this article, we will guide you through the process of understanding permalinks, common issues you might face, and how to fix them. By the end of this article, you will be able to troubleshoot and fix any “WordPress Permalinks Not Working” issue with ease.

WordPress permalinks are the permanent URLs that point to your website’s individual pages, posts, and other content. They are an essential part of your website’s architecture and play a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO). However, sometimes WordPress permalinks are not working as expected. This can cause a lot of frustration for website owners and developers.
Understanding Permalinks in WordPress
WordPress permalinks are the permanent URLs that point to your website’s individual pages, posts, and other content. They are an essential part of your website’s architecture and play a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO). A well-designed permalink structure can enhance the user experience by making it easier for visitors to find and share your content, and it can improve your site’s visibility in search engines by incorporating relevant keywords into the URL. However, sometimes WordPress permalinks are not working as expected. This can cause a lot of frustration for website owners and developers.
By default, WordPress uses a simple permalink structure that includes the post ID and date. However, this structure is not very user-friendly or SEO-friendly. Fortunately, WordPress allows you to customize your permalinks to include more descriptive and relevant information, such as the post title or category. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of permalinks in WordPress and how to customize them to suit your needs.
What are permalinks?
Permalinks are the permanent URLs of your WordPress website’s pages, posts, and other content types. They are also known as “pretty URLs” because they make your website’s URLs human-readable and descriptive. Permalinks are important because they not only help your website visitors easily identify what your content is about, but also help search engines to understand your website’s structure and content hierarchy. When permalinks are not working in WordPress, it can cause a number of issues, including broken links and 404 errors.
Importance of permalinks in SEO
Permalinks play a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO). A permalink that is concise, clear, and includes relevant keywords can help search engines understand the content on your website and rank it higher in search results. Using descriptive and meaningful permalinks can also make it easier for users to understand the content of your pages and navigate your website. In addition, permalinks are used as a basis for backlinks, which are links from other websites that point to your content. If the permalink is relevant and easy to remember, other websites are more likely to link back to your content, which can further improve your website’s SEO. It’s important to understand the importance of permalinks in SEO and take the time to customize them for optimal results.
Default permalink structure
When you first install WordPress, the default permalink structure is set to “Plain” which means that the URL of each page or post on your site will end with a query string, such as “?p=123”. This is not very user-friendly and can negatively impact your site’s SEO. Therefore, it is recommended that you change the default permalink structure to a more descriptive one that includes relevant keywords. However, keep in mind that changing the permalink structure of an established website can also have negative effects, so it is important to plan and implement these changes carefully.
Customizing permalinks
While the default permalink structure in WordPress works fine for most websites, it might not be ideal for every situation. Luckily, WordPress offers a range of customization options that allow you to tailor permalinks to your specific needs.
To customize your permalinks, you need to go to the WordPress dashboard and navigate to the “Permalinks” page under the “Settings” menu. Here, you can choose from a number of preset permalink structures, or you can create your own custom structure by entering a specific combination of tags.
The available tags allow you to include various information in your permalink, such as the post title, date, author, category, and more. By customizing your permalinks, you can make them more descriptive, user-friendly, and optimized for SEO.
It’s worth noting that once you’ve customized your permalink structure, it’s important not to change it frequently, as doing so can result in broken links and negatively impact your site’s SEO.
Common Issues: WordPress Permalinks Not Working
WordPress permalinks are an essential aspect of creating a search engine optimized website. However, sometimes, they may not work as intended, causing problems such as 404 errors, broken links, incorrect permalink URL structures, and even the infamous “white screen of death.” These issues can affect your website’s search engine rankings and user experience, so it’s crucial to fix them as soon as possible. In the next section, we’ll explore some of the most common issues related to WordPress permalinks and how to resolve them.
404 Error
One of the most common issues when WordPress permalinks are not working is the 404 error, which means that the server cannot find the requested page. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including incorrect permalink structure, missing or broken links, or a conflict with a plugin or theme.
A 404 error can be frustrating for users and can negatively impact SEO, as search engines may consider it a broken link and lower the ranking of the page. Therefore, it’s important to resolve this issue as soon as possible.
Broken Links
So called “Broken links” can be another reason why permalinks in WordPress are not working. Broken links occur when a link points to a page or resource that is no longer available or has been moved to a different location. Broken links can happen due to various reasons, such as the deletion of a page, a change in the URL structure, or a server error. When permalinks are not working due to broken links, users will see a 404 error page or encounter other issues when trying to access the page.
To fix broken links, it’s important to regularly check for broken links on your website using a link checker tool. Once you identify the broken links, you can either update the link with the new URL if the page has been moved, or remove the link if the page has been deleted. It’s also a good practice to set up a custom 404 error page that provides users with helpful information and suggests other relevant pages on your website.
By fixing broken links, you can ensure that your website visitors have a better user experience and improve your website’s SEO.
Incorrect Permalink URL structure
Incorrect permalink URL structure is another common issue that can cause WordPress permalinks not to work properly. If the permalink structure is incorrect, it can lead to broken links and a 404 error. One reason for an incorrect permalink URL structure is when WordPress is installed in a subdirectory of the web server’s root directory. In this case, the permalink structure needs to include the subdirectory path. Another reason for an incorrect permalink structure is if a user manually edits the URL slug of a post or page. If the slug is changed without updating the permalink structure, it can lead to broken links.
To fix this issue, users can reset the permalink structure or modify it to match the correct URL structure.
White Screen of Death
The “White Screen of Death” (WSOD) is a common issue in WordPress.It can be caused by problems with permalinks. When a WSOD occurs, the entire screen goes blank, making it difficult to determine the source of the problem. It can be caused by a number of issues, including:
- Problems with plugins or themes
- Insufficient memory
- Issues with the database.
- Incorrect or corrupted permalinks (which can result in a loop that causes the site to crash)
When a WSOD occurs, it is important to troubleshoot the issue to determine the root cause of the problem.

How to Fix WordPress Permalinks Not Working
If you’re facing issues with your WordPress permalinks, there are several steps you can take to fix them. Here are some common methods to try:
Method 1: Reset Permalinks Structure
If your permalinks suddenly stop working, resetting the permalink structure is the first thing you should try. This process is quick and easy, and often resolves the issue.
To reset the permalink structure, log in to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Settings → Permalinks. From there, you can choose any permalink structure and click Save Changes. This will reset your permalink structure to the default settings.
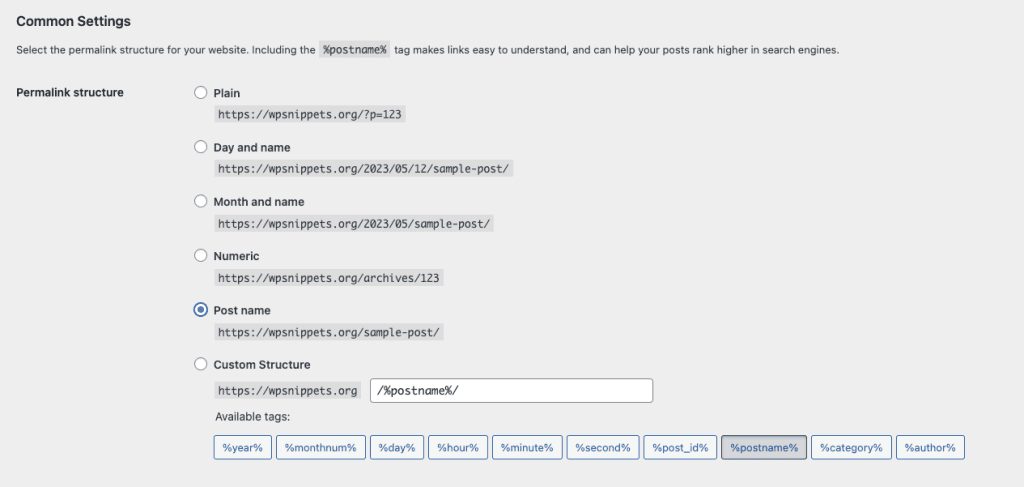
After resetting the permalink structure, try accessing your pages and posts to see if the issue has been resolved. If not, there may be other issues that need to be addressed.
Method 2: Disable Plugins
If resetting the permalink structure did not solve the problem, disabling plugins could be the next solution to try. In some cases, plugins can conflict with the permalink structure and cause issues with the site’s URL structure.
To disable plugins, go to the WordPress dashboard and navigate to the “Plugins” section. From there, you can select all plugins and click the “Deactivate” button. Once all plugins are disabled, try checking the site’s URL structure again.
If the permalink structure works properly after disabling plugins, it’s recommended to reactivate the plugins one by one to identify the plugin causing the issue. Once you find the conflicting plugin, you can either replace it with an alternative or contact the plugin developer for support.
Method 3: Reset .htaccess File
If resetting the permalink structure and disabling plugins does not work, another solution to fix the permalinks in WordPress is to reset the .htaccess file. The .htaccess file is a configuration file that controls how a web server responds to requests. WordPress uses this file to manipulate the URL structure to provide pretty permalinks.
To reset the .htaccess file, first, access the file via FTP or cPanel File Manager. Rename the existing .htaccess file to something else, for example, .htaccess_old. Then, go to the WordPress admin panel, navigate to the Settings -> Permalinks page and click the Save Changes button. This will generate a new .htaccess file with the correct rewrite rules.
After resetting the .htaccess file, check if the permalinks issue is resolved. If not, there might be some other underlying issue causing the problem. In that case, it’s time to troubleshoot.
Troubleshoot WordPress Permalinks Not Working
When troubleshooting issues with permalinks in WordPress, there are several steps you can take to identify and resolve the problem. Here are some tips to help you get started:
Checking the .htaccess file
When WordPress permalinks aren’t working, one of the first things to check is the .htaccess file. This file is responsible for directing the server on how to handle requests for specific URLs. If the file is missing or corrupted, it can cause issues with permalinks. To check the .htaccess file, you can use an FTP client or cPanel file manager to navigate to the root directory of your WordPress site and look for the file. If it’s not there, you can create a new one by going to Settings > Permalinks in your WordPress dashboard and clicking “Save Changes” to generate a new .htaccess file with the correct structure. If the file is present but still causing issues, you can try renaming it to something like “.htaccess_old” and then go to Settings > Permalinks and click “Save Changes” again to generate a new file.
Modifying the permalink structure
If you have tried resetting the permalink structure and disabling plugins but are still facing issues with WordPress permalinks not working, modifying the permalink structure might help.
To do this, go to the Permalinks settings page in your WordPress dashboard and select a different permalink structure. Save the changes and try accessing your website to see if the issue is resolved. If you still experience issues, try using a different permalink structure. For example, if you were using the “post name” structure, try switching to “plain” or “numeric” structure. If this resolves the issue, it might be an issue with your server configuration, and you should contact your hosting provider for assistance.
Disabling conflicting plugins
Sometimes, plugins installed on a WordPress site can interfere with the proper functioning of permalinks. Conflicting plugins can cause issues with the permalink structure or even disable permalinks entirely. To troubleshoot this issue, disabling the plugins temporarily is often recommended.
First, deactivate all the plugins on your WordPress site, then navigate to the permalink settings page and check if the issue has been resolved. If it has, then reactivate the plugins one by one until you identify the plugin causing the issue. Once you identify the problematic plugin, either remove it or find an alternative plugin that does not cause any permalink issues.
If the issue is not resolved after the above steps, the problem may be with the WordPress core files or other server-side issues.
Check your Apache configuration
If you’re using an Apache server, misconfiguration in the server can sometimes cause issues with permalinks in WordPress. In such cases, it’s important to check the server configuration to ensure that it’s properly set up for WordPress.
To do this, you need to open the Apache configuration file and make sure it has the correct settings for WordPress. The location of the file depends on your server setup, but it is often found in /etc/apache2/sites-available/ or /etc/httpd/conf.d/. Once you locate the file, you can use a text editor to open it and make the necessary changes.
Make sure that the configuration file has the following settings:
AllowOverride All
Options FollowSymLinksIf these settings are not present, you need to add them to the configuration file. Once you’ve made the changes, save the file and restart Apache for the changes to take effect. If the issue persists, it’s best to seek the help of an experienced developer or a web hosting support team.
Check your Nginx server
If you’re using Nginx as your web server instead of Apache, you’ll need to make sure that your server is properly configured to handle WordPress permalinks. Here are some steps you can take to troubleshoot permalinks issues on Nginx:
- Check your Nginx configuration file. Start by checking your Nginx configuration file to make sure it includes the necessary directives to support permalinks. You’ll need to include the following lines in your server block:
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}This tells Nginx to check if the requested file or directory exists. And, if it doesn’t, to pass the request to WordPress for handling.
- Test your configuration. Once you’ve updated your Nginx configuration file, test to see if your permalinks are working correctly. If they’re not, you may need to modify your configuration file further to ensure that Nginx is properly passing requests to WordPress.
- Check your caching plugin. If you’re using a caching plugin, it may be interfering with your permalinks. Try disabling your caching plugin and see if that resolves the issue. If it does, you may need to adjust the caching plugin’s settings to work with your permalinks.
- Update WordPress. Make sure you’re using the latest version of WordPress, as older versions may not be compatible with the latest versions of Nginx.
By following these steps, you should be able to troubleshoot and fix any permalink issues you’re experiencing on Nginx.
Updating WordPress and plugins
Keeping WordPress and its plugins up-to-date is essential to ensure the proper functioning of your website. An outdated version of WordPress or a plugin can cause conflicts and result in permalink issues.
To update WordPress and its plugins, log in to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to the “Updates” section. Here, you will see a list of available updates for WordPress and your plugins. Click “Update Now” for each update, and WordPress will take care of the rest.
It is important to note that before updating, you should make a backup of your website to avoid any potential data loss in case of unexpected errors during the update process.
Debugging using the WP_DEBUG function
If you’ve tried all the methods mentioned above and are still experiencing issues with your WordPress permalinks, you can try debugging using the WP_DEBUG function. This function will display any errors or warnings on your website, helping you identify the root cause of the problem.
To enable WP_DEBUG, you need to add the following line of code to your wp-config.php file:
define( 'WP_DEBUG', true );This will enable debugging mode in WordPress. You should now be able to see any error messages on your website, including issues related to permalinks.
It’s important to note that we don’t recommend leaving WP_DEBUG enabled on a live website, as it can expose sensitive information to your visitors. Therefore, once you’ve identified and fixed the issue, make sure to turn WP_DEBUG off by changing the value to false:
define('WP_DEBUG', false);Debugging using WP_DEBUG can be a helpful tool in identifying issues related to permalinks or other aspects of your WordPress site.
Resolving Specific Permalinks Issues
In addition to the general solutions mentioned above, some specific permalink issues require more targeted solutions. In this section, we will look at how to resolve some of the most common specific permalink issues.
Category and Tag Base Missing
If you notice that category and tag archive pages are not working, it may be because the category or tag base is missing. Here’s how you can fix this issue. Go to Settings > Permalinks in your WordPress dashboard and add a custom base for your categories and tags. For example, if you want your category base to be “topic,” you would add “/topic” as the custom base. If you want to remove the /category/ base from the URL, see this snippet: Remove Category from URL / Permalink.
Removing index.php from URLs
If you want to remove the index.php from your WordPress URLs, you either don’t have pretty permalinks enabled, or you might need to make some changes to your site’s .htaccess file. See our guide: Remove index.php from URL.
Adding or removing trailing slash in the URL
Adding or removing a trailing slash in URLs can be helpful in some cases. By default, WordPress does not add a trailing slash to the URLs. However, some web servers or caching systems may require it for correct URL routing. Add a trailing slash to all URLs using the following code snippet: Add a Trailing Slash To the URL. Remove a trailing slash from all URLs using the following code snippet: Remove Trailing Slash from URL.
Removing /category/ base from Permalinks
By default, WordPress adds “/category/” to your category archive URLs. If you want to remove this and make your category archive URLs shorter, you can use our code snippet: Remove Category from URL / Permalink.
404 Error on Custom Post Type
If you are having issues with custom post type permalinks not working, it may be because you have not set up the rewrite rules for your custom post type correctly. When you’re registering a custom post type manually, make sure you’re using the right value for the rewrite array key in the arguments.
If you are getting a 404 error on your custom post type archive pages, it may be because you have not set up the rewrite rules for your custom post type archive pages correctly. To fix this issue, you can use this code snippet, replacing “custom_post_type” with the name of your custom post type:
function custom_post_type_archive( $query ) {
if ( is_post_type_archive( 'custom_post_type' ) && ! is_admin() && $query->is_main_query() ) {
$query->set( 'post_type', 'custom_post_type' );
}
}
add_action( 'pre_get_posts', 'custom_post_type_archive' );Using permalinks with FSE (full site editing) and Gutenberg
Permalinks with Full Site Editing (FSE) and Gutenberg work in the same way as with the classic editor. However, if you’re using FSE, you need to ensure that you’re using a theme that supports FSE. In FSE, the theme’s template hierarchy and template parts take care of the URL structure. This means that you don’t need to modify the permalink settings. In other words, you can leave the permalink settings at their default settings. However, if you’re using custom post types, taxonomies, or custom fields, you may need to create custom templates or modify the existing ones to ensure that the permalinks work correctly.
When using Gutenberg, the permalink settings are located in the document settings sidebar. Simply click on the document settings icon (the “i” icon) in the top right-hand corner of the screen, and then click on “Permalink” to modify the URL structure for the page or post you’re working on.
Overall, permalinks work the same way in FSE and Gutenberg as they do in the classic editor. However, it’s essential to ensure that you set up your theme and any custom post types, taxonomies, or custom fields correctly to avoid any issues with your URL structure.
Advanced Techniques for Managing Permalinks
Managing permalinks can be tricky at times. However, there are several advanced techniques that you can use to further enhance your control over your WordPress site’s permalink structure.
Redirect broken or updated links
Sometimes, you may need to change the permalink structure of a page or post. This could result in broken links if other websites or search engines are linking to the old URL. In such cases, you can use redirect rules to ensure that you redirect visitors to the new URL. By redirecting your broken links, you can:
- Redirect your old permalinks to new ones
- Update your permalink structure
- Keep your SEO juice intact.
Even while setting up redirects can be helpful, it’s not a substitute for fixing the root cause of the issue. If your permalinks are not working correctly, you should try to resolve the underlying issue. Relying relying solely on redirects is not a good practice.
Custom rewrite rules and endpoints
In addition to customizing permalinks using the WordPress settings or modifying the .htaccess file, you can also add custom rewrite rules and endpoints to your site’s permalinks. Custom rewrite rules allow you to create specific URL patterns for your pages, posts, or other content types. See the following snippets for more information: Custom Rewrite Endpoint and Custom Rewrite Rules.
Working with JSON files to modify permalinks
WordPress provides the option to modify permalinks through the interface or by updating the .htaccess file, but there’s an even more advanced way to manage permalinks using JSON files. WordPress introduced JSON files as a way to configure different aspects of a site programmatically. In the case of permalinks, you can use the permalink_structure key in the wp_options object to set the desired permalink structure.
To get started, create a JSON file named permalink.json with the following code:
{
"permalink_structure": "/%year%/%monthnum%/%postname%/"
}In this example, we set the permalink structure to include the year, month, and post name. You can modify this to fit your needs. Next, upload this file to your WordPress site’s root directory, typically where you find the wp-config.php file. Once you’ve uploaded the file, you can update the permalink structure by running the following WP-CLI command:
wp option patch update permalink < permalink.jsonThis command will read the contents of permalink.json and update the permalink_structure key in the wp_options object accordingly.
Using JSON files to manage permalinks provides a more flexible and programmatic approach to managing permalink structures. It’s particularly useful if you have a large number of sites or want to manage permalinks through scripts or code.
Best Practices for Optimizing Permalink Structure
Optimizing the permalink structure on your WordPress site can help improve your website’s SEO and make it easier for users to navigate. Here are some best practices for optimizing your WordPress permalink structure:
- Keep it simple: Use short, descriptive and easy-to-remember permalinks that include your target keywords. Avoid using special characters, symbols or stop words in your permalinks.
- Use categories and tags: Categorizing your content and using relevant tags can help organize your website’s content and make it easier for users to navigate.
- Avoid changing permalinks: Once you have set up your permalinks, avoid changing them as this can result in broken links and negatively impact your website’s SEO.
- Use HTTPS: Use HTTPS in your permalinks to ensure that your website is secure and that search engines recognize it as a secure site.
- Avoid duplicate content: Be careful not to create duplicate content by using the same permalink for multiple pages or posts.
- Use canonical URLs: Use canonical URLs to tell search engines which URL is the primary version of a page to avoid duplicate content issues.
- Test your permalinks: Regularly test your permalinks to ensure that they are functioning correctly and that there are no broken links.
- Keep it short and simple: Avoid using complicated or lengthy structures. Long permalinks can be difficult for users to remember and can also look spammy. Aim for a concise and easy-to-remember permalink. A simple structure using only relevant keywords is best.
- Use descriptive keywords: Including relevant keywords in your permalinks helps search engines and users understand what your content is about.
- Don’t change permalinks frequently: Changing permalinks frequently can negatively affect your site’s SEO. If you do need to change permalinks, set up redirects to avoid broken links.
- Avoid stop words and special characters: Words like “and,” “a,” “the,” etc. add unnecessary length to your permalinks, and you should skip these. Special characters such as symbols, punctuation marks, and non-ASCII characters can create issues for search engines and web crawlers. Stick to alphanumeric characters when possible.
- Test your permalinks: Make sure your permalinks are working correctly and don’t lead to 404 errors or other issues.
- Use hyphens to separate words: When creating permalinks, use hyphens to separate words instead of underscores or spaces. Hyphens are more SEO-friendly and can help search engines understand the content of your page more easily.
- Make permalinks human-readable: Make sure your permalinks are easy for users to read and understand. Avoid using random strings of letters and numbers, and instead use descriptive words that accurately reflect the page’s content.
Importance of testing permalinks after making changes
It is crucial to test permalinks after making any changes to the permalink structure. Even small modifications can cause links to break and lead to 404 errors. It’s a good practice to regularly test permalinks on your site to ensure that they are working as intended. One way to do this is to click on each link on your site and make sure that it leads to the correct page without any errors. Additionally, you can use tools such as Google Search Console to identify any crawl errors and fix them promptly.
By regularly testing and monitoring your permalinks, you can ensure that your website’s URL structure remains optimized for both users and search engines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, permalinks are a critical aspect of WordPress that contribute significantly to SEO and user experience. Customizing your permalinks can enhance your website’s readability and make it easier for users to navigate your site. However, issues with permalinks can cause various problems, such as broken links and 404 errors. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can identify and resolve these issues efficiently. Remember to test your permalinks after making any changes and use descriptive keywords in your URLs for optimal SEO results. Finally, always ensure the security of your permalinks and the privacy of your users. By implementing these best practices, you can ensure that your WordPress website’s permalinks are optimized for both user experience and search engine optimization.